Online first
About the Journal
Current issue
Archive
Publication Ethics
Anti-Plagiarism system
Instructions for Authors
Instructions for Reviewers
Editorial Office
Editorial Board
Contact
Reviewers
All Reviewers
2025
2024
2023
2022
2021
2020
2019
2018
2017
2016
General Data Protection Regulation (RODO)
REVIEW PAPER
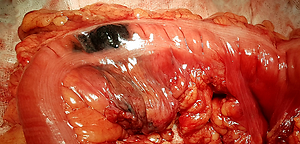
Application of endoscopic tattooing in intraoperative localization of colon tumours and sentinel lymph nodes
1
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy Unit, Medical University, Lublin, Poland
2
2nd Department of General Surgery, Medical University, Lublin, Poland
Corresponding author
Norbert Nowak
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy Unit, Medical University of Lublin, Poland., Staszica 16, 20-081, Lublin, Poland
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy Unit, Medical University of Lublin, Poland., Staszica 16, 20-081, Lublin, Poland
J Pre Clin Clin Res. 2020;14(4):134-138
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Minimally invasive techniques in colorectal surgery have become increasingly popular and are considered a standard of care in most surgical cenres. Locating the tumour during laparoscopic procedure can be technically challenging. Incorrect localization of the primary lesion may lead to a non-radical resection margin. The technique of endoscopic tattooing (ET) prior to surgery or endoscopic treatment is considered a useful tool. Various dyes can be used for this purpose, such as: Indian ink, methylene blue, indigocarmine, toluidine blue, isosulfan blue, haematoxylin and eosin, indoxin green. This procedure is recommended by international scientific societies (ASGE and ESGE).
Objective:
The purpose of the study is to review the current literature on the use of ET in large intestine tumour lesions.
Material and Methods:
A MEDLINE literature search of English language articles addressing the use of ET to enable intraoperative tumour localization in colorectal surgery was performed to evaluate and summarize the feasibility of this technique.
Results:
The use of ET enables the easy and safe localization of colorectal tumurs during minimally invasive colorectal procedures. The percentage of complications is insignificant.
Conclusions:
The available literature proves the safety and benefits of using the ET prior to surgical or endoscopic treatment. ASGE and ESGE recommend the use of ET in marking tumours before surgical treatment, and the area after endoscopic resection for further evaluation.
Minimally invasive techniques in colorectal surgery have become increasingly popular and are considered a standard of care in most surgical cenres. Locating the tumour during laparoscopic procedure can be technically challenging. Incorrect localization of the primary lesion may lead to a non-radical resection margin. The technique of endoscopic tattooing (ET) prior to surgery or endoscopic treatment is considered a useful tool. Various dyes can be used for this purpose, such as: Indian ink, methylene blue, indigocarmine, toluidine blue, isosulfan blue, haematoxylin and eosin, indoxin green. This procedure is recommended by international scientific societies (ASGE and ESGE).
Objective:
The purpose of the study is to review the current literature on the use of ET in large intestine tumour lesions.
Material and Methods:
A MEDLINE literature search of English language articles addressing the use of ET to enable intraoperative tumour localization in colorectal surgery was performed to evaluate and summarize the feasibility of this technique.
Results:
The use of ET enables the easy and safe localization of colorectal tumurs during minimally invasive colorectal procedures. The percentage of complications is insignificant.
Conclusions:
The available literature proves the safety and benefits of using the ET prior to surgical or endoscopic treatment. ASGE and ESGE recommend the use of ET in marking tumours before surgical treatment, and the area after endoscopic resection for further evaluation.
FUNDING
No funding was received for the study.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Nowak N, Dziedzic J, Nurczyk K, Zakościelny A, Bury P, Zgodziński W, Zinkiewicz K. Application of endoscopic tattooing in intraoperative localization of colon tumors and sentinel lymph nodes. J Pre-Clin Clin Res. 2020; 14(4): 134–138. doi: 10.26444/jpccr/128226
REFERENCES (61)
1.
Elarini T, Wexner SD, Isenberg GA. The need for standardization of colonoscopic tattooing of colonic lesions. Dis Colon Rectum. 2015; 58(2): 264–7.
2.
Ponsky JL, King JF. Endoscopic marking of colonic lesions. Gastrointest Endosc. 1975; 22(1): 42–3.
3.
Ferlitsch M, Moss A, Hassan C, et al. Colorectal polypectomy and endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR): European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Clinical Guideline. Endoscopy. 2017 Mar; 49(3): 270–297. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-102569. Epub 2017 Feb 17. PMID: 28212588.
4.
Conaghan PJ, Maxwell-Armstrong CA, Garrioch MV, Hong L, Acheson AG. Leaving a mark: the frequency and accuracy of tattooing prior to laparoscopic colorectal surgery. Colorectal Dis. 2011; 13(10): 1184–7.
5.
Aboosy N, Mulder CJ, Berends FJ, Meijer JW, Sorge AA. Endoscopic tattoo of the colon might be standardized to locate tumors intraoperatively. Rom J Gastroenterol. 2005; 14(3): 245–8.
6.
ASGE Technology Committee, Kethu SR, Banerjee S, et al. Endoscopic tattooing. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 72(4): 681–5.
7.
Fu KI, Fujii T, Kato S, et al. A new endoscopic tattooing technique for identifying the location of colonic lesions during laparoscopic surgery: a comparison with the conventional technique. Endoscopy. 2001; 33(8): 687–691.
8.
Sawaki A, Nakamura T, Suzuki T, et al. A two-step method for marking polypectomy sites in the colon and rectum. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 57(6): 735–737.
9.
Nizam R, Siddiqi N, Landas SK, Kaplan DS, Holtzapple PG. Colonic tattooing with India ink: benefits, risks, and alternatives. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996; 91(9): 1804–1808.
10.
Shatz BA, Weinstock LB, Swanson PE, Thyssen EP. Long-term safety of India ink tattoos in the colon. Gastrointest Endosc. 1997; 45(2): 153–156.
11.
Hammond DC, Lane FR, Welk RA, Madura MJ, Borreson DK, Passinault WJ. Endoscopic tattooing of the colon. An experimental study. Am Surg. 1989; 55(7): 457–461.
12.
Price N, Gottfried MR, Clary E, et al. Safety and efficacy of India ink and indocyanine green as colonic tattooing agents. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000; 51(4 Pt 1): 438–442.
13.
Gress FG, Barawi M, Kim D, Grendell JH. Preoperative localization of a neuroendocrine tumor of the pancreas with EUS-guided fine needle tattooing. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 55(4): 594–597.
14.
Farrell JJ, Sherrod A, Parekh D. EUS-guided fine-needle tattooing for preoperative localization of early pancreatic adeno carci noma. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69(1): 176–177.
15.
Wiklund L, Basu S, Miclescu A, Wiklund P, Ronquist G, Sharma HS. Neuro- and cardioprotective effects of blockade of nitric oxide action by administration of methylene blue. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007; 1122: 231–244.
16.
Liu J, Huang P, Zheng Z, Chen T, Wei H. Modified methylene blue injection improves lymph node harvest in rectal cancer. ANZ J Surg. 2017; 87(4): 247–251.
17.
Bara T Jr, Gurzu S, Jung I, Borz C, Banias L, Bara T. Sentinel node biospy using intravital blue dye: An useful technique for identification of skip metastases in gastric cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019; 98(12): e14951.
18.
Craik D, Khan D, Afifi R. The safety of intravenous indigo carmine to assess ureteric patency during transvaginal uterosacral suspension of the vaginal vault. Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery, 2009; 15(1): 11–15.
19.
Retter J, Collet PH, Böcker U, Singer MV, Kähler G. Toluidinblau in der gastrointestinalen Endoskopie [Toluidin blue in gastrointestinal endoscopy]. Z Gastroenterol. 2010; 48(9): 1117–1119.
20.
Rivet EB, Mutch MG, Ritter JH, et al. Ex vivo sentinel lymph node mapping in laparoscopic resection of colon cancer. Colorectal Dis. 2011; 13(11): 1249–1255.
21.
Kane JM 3rd, Kahlenberg MS, Rodriguez-Bigas MA, Gibbs JF, Petrelli NJ. Intraoperative hepatic lymphatic mapping in patients with liver metastases from colorectal carcinoma. Am Surg. 2002; 68(9): 745–750.
22.
Lee JY, Kim N. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori by invasive test: histology. Ann Transl Med. 2015; 3(1): 10.
23.
Ortiz-Fernandez-Sordo J, Sami SS, Mansilla-Vivar R, et al. Evaluation of a novel infra-red endoscopy system in the assessment of early neoplasia in Barretts esophagus: pilot study from a single center [published correction appears in Dis Esophagus. 2018 Apr 1; 31(4):]. Dis Esophagus. 2018; 31(3): 10.1093/dote/dox137.
24.
Karakatsanis A, Christiansen PM, Fischer L, et al. The Nordic Senti-Mag trial: a comparison of super paramagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) nanoparticles versus Tc(99) and patent blue in the detection of sentinelnode (SN) in patients with breast cancer and a meta-analysis of earlier studies. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016; 157(2): 281–294.
25.
Teshome M, Wei C, Hunt KK, Thompson A, Rodriguez K, Mittendorf EA. Use of a Magnetic Tracer for Sentinel Lymph Node Detection in Early-Stage Breast Cancer Patients: A Meta-analysis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016; 23(5): 1508–1514.
26.
Houpeau JL, Chauvet MP, Guillemin F, et al. Sentinel lymph node identification using superparamagnetic iron oxide particles versus radioisotope: The French Sentimag feasibility trial. J Surg Oncol. 2016; 113(5): 501–507.
27.
Ghilli M, Carretta E, Di Filippo F, et al. The superparamagnetic iron oxide tracer: a valid alternative in sentinel node biopsy for breast cancer treatment. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). 2017; 26(4): 10.1111/ecc.12385.
28.
Piñero-Madrona A, Torró-Richart JA, de León-Carrillo JM, et al. Superparamagnetic iron oxide as a tracer for sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer: A comparative non-inferiority study. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2015; 41(8): 991–997.
29.
Rubio IT, Diaz-Botero S, Esgueva A, et al. The superparamagnetic iron oxide is equivalent to the Tc99 radiotracer method for identifying the sentinel lymph node in breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2015; 41(1): 46–51.
30.
Thill M, Kurylcio A, Welter R, et al. The Central-European SentiMag study: sentinel lymph node biopsy with superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) vs. radioisotope. Breast. 2014; 23(2): 175–179.
31.
Douek M, Klaase J, Monypenny I, et al. Sentinel node biopsy using a magnetic tracer versus standard technique: the SentiMAG Multicentre Trial. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014; 21(4): 1237–1245.
32.
Winter A, Woenkhaus J, Wawroschek F. A novel method for intra-operative sentinel lymph node detection in prostate cancer patients using superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and a handheld magnetometer: the initial clinical experience. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014; 21(13): 4390–4396.
33.
ten Haken B. et al. (2010) Magnetic Detection of the Sentinel Lymph Node in Ex Vivo Tissue with Colorectal Cancer. In: Supek S., Sušac A. (eds) 17th International Conference on Biomagnetism Advances in Biomagnetism – Biomag2010. IFMBE Proceedings, vol 28. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
34.
Gonzalez-Tallon AI, Rivero-Fernandez M, Calvo-Ramos I, et al. Hematemesis With Gastric Laceration After Tattooing a Polyp With Purified Carbon: A Review of the Literature. Gastroenterology Res. 2017; 10(1): 45–49.
35.
Park SI, Genta RS, Romeo DP, Weesner RE. Colonic abscess and focal peritonitis secondary to india ink tattooing of the colon. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991; 37(1): 68–71.
36.
Bang CS, Kim YS, Baik GH, Han SH. Colonic abscess induced by India ink tattooing. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2014; 64(1): 45–48.
37.
Alba LM, Pandya PK, Clarkston WK. Rectus muscle abscess associated with endoscopic tattooing of the colon with India ink. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000; 52(4): 557–558.
38.
Singh S, Arif A, Fox C, Basnyat P. Complication after pre-operative India ink tattooing in a colonic lesion. Dig Surg. 2006; 23(5–6): 303.
39.
Aawsaj YM, Kelly S, Slater B. Liver abscess secondary to an endoscopic tattoo in the colon. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2017; 99(2): e47–e48.
40.
Marques I, Lagos AC, Pinto A, Neves BC. Rectal intramural hematoma: a rare complication of endoscopic tattooing. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 73(2): 366–367.
41.
Dell’Abate P, Iosca A, Galimberti A, Piccolo P, Soliani P, Foggi E. Endoscopic preoperative colonic tattooing: a clinical and surgical complication. Endoscopy. 1999; 31(3): 271–273.
42.
Coman E, Brandt LJ, Brenner S, Frank M, Sablay B, Bennett B. Fat necrosis and inflammatory pseudotumor due to endoscopic tattooing of the colon with india ink. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991; 37(1): 65–68.
43.
Gopal DV, Morava-Protzner I, Miller HA, Hemphill DJ. Idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease associated with colonic tattooing with india ink preparation--case report and review of literature. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999; 49(5): 636–639.
44.
Bahadursingh AM, Driver M, Koenig CL, Longo WE. Inadvertent transmural India ink tattooing simulating intestinal infarction. Am J Surg. 2003; 185(1): 88–89.
45.
Gianom D, Hollinger A, Wirth HP. Darmperforation nach präoperativer kolonoskopischer Tuschemarkierung [Intestinal perforation after preoperative colonic tattooing with India ink]. Swiss Surg. 2003; 9(6): 307–310.
46.
Chen N, Lamba R, Lee J, Lall C. Mesenteric air embolism following enteroscopic small bowel tattooing procedure. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2012; 2: 86.
47.
Park SI, Genta RS, Romeo DP, Weesner RE. Colonic abscess and focal peritonitis secondary to India ink tattooing of the colon. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991; 37: 68–71.
48.
Moss A, Bourke MJ, Pathmanathan N. Safety of colonic tattoo with sterile carbon particle suspension: a proposed guideline with illustrative cases. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011 Jul; 74(1): 214–8. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2011.01.056. Epub 2011 Apr 8. PMID: 21481865.
49.
Bartels SAL, van der Zaag ES, Dekker E, Buskens CJ, Bemelman WA. The effect of colonoscopic tattooing on lymph node retrieval and sentinel lymph node mapping. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 76: 793–800. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2012.05.005.
50.
Aldecoa I, et al. Endoscopic tattooing of early colon carcinoma enhances detection of lymph nodes most prone to harbor tumor burden, Surg Endosc. 2017; 31(2): 723–733. 10.1007/s00464-016-5026-3.
51.
Ellis KK, Fennerty MB. Marking and identifying colon lesions. Tattoos, clips, and radiology in imaging the colon. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 1997; 7: 401–411.
52.
Yeung JMC, Maxwell-Armstrong C, Acheson AG. Colonic tattooing in laparoscopic surgery—making the mark? Colorectal Dis. 2009; 11: 527–530. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1318.2008.01706.x.
53.
Beretvas RI, Ponsky J. Endoscopic marking: an adjunct to laparoscopic gastrointestinal surgery. Surg Endosc. 2001; 15: 1202–1203. doi: 10.1007/s004640000304.
54.
Lacy AM, García-Valdecasas JC, Delgado S, Castells A, Taurá P, Piqué JM, Visa J. Laparoscopy-assisted colectomy versus open colectomy for treatment of non-metastatic colon cancer: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2002; 359: 2224–2229. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)09290-5.
55.
Dawson K, Wiebusch A, Thirlby RC. Preoperative tattooing and improved lymph node retrieval rates from colectomy specimens in patients with colorectal cancers. Arch Surg. 2010; 145: 826–830. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.2010.180.
56.
Kang J, Park HS, Kim I, Song Y, Baik SH, Sohn S-K, Lee KY. Effect of preoperative colonoscopic tattooing on lymph node harvest in T1 colorectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2015; 30: 1349–1355. doi: 10.1007/s00384-015-2308-5.
57.
Feo CV, Portinari M, Zuolo M, Targa S, Matarese VG, Gafà R, Forini E, Lanza G. Preoperative endoscopic tattooing to mark the tumour site does not improve lymph node retrieval in colorectal cancer: a retrospective cohort study. J Negat Results Biomed. 2015; 14: 9. doi: 10.1186/s12952-015-0027-7.
58.
Spatz H, Probst A, Oruzio D, Anthuber M, Messmann H, Arnholdt HM, Märkl B. Sentinel lymph node mapping as a side-effect of colonoscopic tattooing. Surg Endosc. 2010; 24: 589–593. doi: 10.1007/s00464-009-0641-x.
59.
Viehl CT, Guller U, Hamel CT, Riehle HM, Plaass C, Marti WR, Oertli D, Zuber M. Carbon dye staining of sentinel lymph nodes facilitates microstaging of colon cancer patients. World J Surg. 2006; 30: 453–456. doi: 10.1007/s00268-005-0336-y.
60.
Cahill RA, Lindsey I, Cunningham C. Sentinel node mapping by colonic tattooing. Surg Endosc Other Interv Tech. 2010; 24: 2365–2366. doi: 10.1007/s00464-010-0941-1.
61.
Keller D, Jaffe J, Philp MM, Haluszka O, Khanna A. Should all endoscopically excised rectal polyps be tattooed? A plea for localization. Surg Endosc Other Interv Tech. 2012; 26: 3101–3105.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.