Online first
About the Journal
Current issue
Archive
Publication Ethics
Anti-Plagiarism system
Instructions for Authors
Instructions for Reviewers
Editorial Office
Editorial Board
Contact
Reviewers
All Reviewers
2025
2024
2023
2022
2021
2020
2019
2018
2017
2016
General Data Protection Regulation (RODO)
CASE REPORT
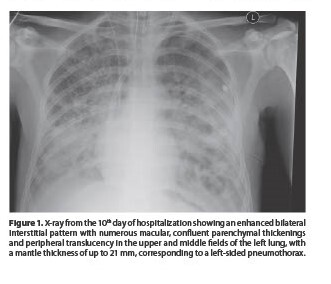
Pneumothorax as a complication of respiratory failure – two case reports and literature review
1
Student Research Group, Second Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Therapy, Medical University, Lublin,
Poland
Corresponding author
Milena Krawczyk
Student Research Group, Second Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Therapy, Medical University of Lublin, Lublin, Poland
Student Research Group, Second Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Therapy, Medical University of Lublin, Lublin, Poland
J Pre Clin Clin Res. 2024;18(2):139-146
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) – severe clinical syndrome with a high mortality rate, is characterized by
hypoxemia and respiratory failure secondary to non-cardiogenic pulmonary oedema. The most common cause of ARDS
is pneumonia. The cases are presented of 2 male patients: a 28-year-old and a 41-year-old, who were in a severe general
condition due to progressive respiratory failure secondary to pneumonia. Despite antibiotic therapy the condition of the
patients deteriorated. A differential diagnosis was performed, in which autoimmune causes, tuberculosis and viral infections
were excluded. During hospitalization, both men developed pneumothorax requiring urgent drainage. A decline and
deterioration of the patients’ vital signs was observed and eventually death was pronounced. ARDS is a severe disease
that poses a challenge in clinical practice. The course of the disease is difficult to predict, and the patient requires intensive
surveillance and treatment.
Krawczyk M, Chajec J, Paluch Z, Michalczyk J, Miłosz A, Szczukocka M. Pneumothorax as a complication of respiratory failure – two case reports and literature review. J Pre-Clin Clin Res. 2024; 18(2): 139–146. doi: 10.26444/jpccr/188770
REFERENCES (39)
1.
Saguil A, Fargo MV. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Diagnosis and Management. Am Fam Physician. 2020;101(12):730–738.
2.
Diamond M, Peniston HL, Sanghavi D. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. StatPearls. https://www.statpearls.com/poi... (access: 2023.12.11).
3.
Williams GW, Berg NK, Reskallah A. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Anesthesiology. 2021;134(2):270–282.
4.
Kuperminc E, Heming N, Carlos M. Corticosteroids in ARDS. J Clin Med. 2023;12(9):33–40.
5.
ARDS Definition Task Force, Ranieri VM, Rubenfeld GD. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin Definition. JAMA. 2012;307(23):2526–2533.
6.
Matthay MA, Arabi Y, Arroliga AC, Bernard G, Bersten AD, Brochard LJ, Calfee CS, Combes A, Daniel BM, Ferguson ND, Gong MN, Gotts JE, Herridge MS, Laffey JG, Liu KD, Machado FR, Martin TR, McAuley DF, Mercat A, Moss M, Mularski RA, Pesenti A, Qiu H, Ramakrishnan N, Ranieri VM, Riviello ED, Rubin E, Slutsky AS, Thompson BT, Twagirumugabe T, Ware LB, Wick KD. A New Global Definition of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024;209(1):37–47.
7.
Meyer NJ, Gattinoni L, Calfee CS. Acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet. 2021;398(10300):622–637.
8.
Kulkarni HS, Lee JS, Bastarache JA. Update on the Features and Measurements of Experimental Acute Lung Injury in Animals: An Official American Thoracic Society Workshop Report. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2022;66(2):e1–e14.
9.
Luyt CE, Bouadma L, Morris AC. Pulmonary infections complicating ARDS. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46(12):2168–2183.
10.
Long ME, Mallampalli RK, Horowitz JC. Pathogenesis of pneumonia and acute lung injury. Clin Sci (Lond). 2022;136(10):747–769.
11.
Peng W, Wu Y, Lu R, Zheng Y, Chen J, Pan P. Successful treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and continuous renal replacement therapy: A case report and literature review. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9,936927.
12.
Shah RD, Wunderink RG. Viral Pneumonia and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Clin Chest Med. 2017;38(1):113–125.
13.
Attaway AH, Scheraga RG, Bhimraj A, Biehl M, Hatipoğ Lu U. Severe covid-19 pneumonia: pathogenesis and clinical management. BMJ. 2021;372–436.
14.
Gibson PG, Qin L, Puah SH. COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): clinical features and differences from typical pre-COVID-19 ARDS. Med J Aust. 2020;213(2):54–56.
15.
Taha M, Elahi M, Wahby K, Samavati L. Incidence and risk factors of COVID-19 associated pneumothorax. PLoS One. 2022;17(8):e0271964.
16.
Terzi E, Zarogoulidis K, Kougioumtzi I. Acute respiratory distress syndrome and pneumothorax. J Thorac Dis. 2014;6(4):435–442.
17.
Nakanishi T, Forgetta V, Handa T. The undiagnosed disease burden associated with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency genotypes. Eur Respir J. 2020;56(6).
18.
Kokturk N, Khodayari N, Lascano J, Riley EL, Brantly ML. Lung Inflammation in alpha-1-antitrypsin deficient individuals with normal lung function. Respir Res. 2023;24(1):40.
19.
Ostermann L, Maus R, Stolper J. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency impairs lung antibacterial immunity in mice. JCI Insight. 2021;6(3).
20.
Bauer M, Fuhrmann V, Wendon J. Pulmonary complications in liver disease. Intensive Care Med. 2019;45(10):1433–1435.
21.
Xu L, Ying S, Hu J, et al. Pneumonia in patients with cirrhosis: risk factors associated with mortality and predictive value of prognostic models. Respir Res. 2018;19(1):242.
22.
Cuomo G, Brancaccio G, Stornaiuolo G. Bacterial pneumonia in patients with liver cirrhosis, with or without HIV co-infection: a possible definition of antibiotic prophylaxis associated pneumonia (APAP). Infect Dis. 2018;50(2):125–132.
23.
Hung TH, Tseng CW, Hsieh YH, Tseng KC, Tsai CC, Tsai CC. High mortality of pneumonia in cirrhotic patients with ascites. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013;13(1):25.
24.
Piotrowski D, Saczewska-Piotrowska A, Boroń-Kaczmarska A, Jaroszewicz J. Lymphocyte-To- Monocyte Ratio as the Best Simple Predictor of Bacterial Infection in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(5):1727.
25.
Gao F, Cai MX, Lin MT, Zhang LZ, Ruan QZ, Huang ZM. Model for end-stage liver disease and pneumonia: An improved scoring model for critically ill cirrhotic patients with pneumonia. The Turkish Journal of Gastroenterology. 2019;30(6):532–540.
26.
Morita H, Shimizu Y, Nakamura Y. Auto-antibody evaluation in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia and worse survival of patients with Ro52/TRIM21auto-antibody. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2020;67(2):199–205.
27.
Bahmer T, Romagnoli M, Girelli F, Claussen M, Rabe KF. The use of auto-antibody testing in the evaluation of interstitial lung disease (ILD) – A practical approach for the pulmonologist. Respir Med. 2016;113:80–92.
28.
Kamp JC, Jonigk DD, Hinrichs JB. Recurrent Life-threatening Pneumonitis in a 37-Year-Old Woman. Chest. 2020;158(3):127–132.
29.
Wu SJ, Hsu YC, Wang KL, Fu PK. Prone Positioning May Improve the Treatment of Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage and Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) Secondary to ANCA Associated Vasculitis: A Case Report. Life (Basel). 2022;12(2):235.
30.
Turgeon D, Balter MS, Pagnoux C. Interstitial lung disease in patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitis: an update on pathogenesis and treatment. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2023;29(5):436–442.
31.
Yildirim Dogan HG, Yildirim F, Icacan OC, Yalcin Mutlu M, Celik S, Bes C. Pulmonary involvement in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitides: A single center experience from Turkey. Int J Rheum Dis. 2023;26(8):1495–1503.
32.
Steward M, Thould H, Myat Noe Khin A, Gibbons MA. Interstitial Lung Disease and Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis: A Review. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2023;43(2):379–388.
33.
Ha JW, Pyo JY, Ahn SS, Song JJ, Park YB, Lee SW. Incidence and Patterns of Interstitial Lung Disease and Their Clinical Impact on Mortality in Patients with Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody- Associated Vasculitis: Korean Single-Centre Observational Study. J Immunol Res. 2022.
34.
Sun K, Fisher JH, Pagnoux C. Interstitial Lung Disease in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: Pathogenic Considerations and Impact for Patients’ Outcomes. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2022;24(8):259–267.
35.
Qadir N, Sahetya S, Munshi L. An Update on Management of Adult Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: An Official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice Guideline. 2023;209(1):24–36.
36.
Lee H, Song MJ, Cho YJ. Supervised machine learning model to predict mortality in patients undergoing venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation from a nationwide multicentre registry. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2023;10(1):002025.
37.
Collins PD, Giosa L, Camporota L, Barrett NA. State of the art: Monitoring of the respiratory system during veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Perfusion. 2024;39(1):7–30.
38.
Diaz D, Martinez J, Bushman G, Wolowich W. Anticoagulation strategies in COVID-19 infected patients receiving ECMO support. J Extra Corpor Technol. 2023;55(3):121–129.
39.
Vajter J, Holubova G, Novysedlak R, Svorcova M, Vachtenheim J Jr, Vymazal T, Lischke R. Anaesthesiologic Considerations for Intraoperative ECMO Anticoagulation During Lung Transplantation: A Single-Centre, Retrospective, Observational Study. Transpl Int. 2024;37:12752.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.