Online first
About the Journal
Current issue
Archive
Publication Ethics
Anti-Plagiarism system
Instructions for Authors
Instructions for Reviewers
Editorial Office
Editorial Board
Contact
Reviewers
All Reviewers
2025
2024
2023
2022
2021
2020
2019
2018
2017
2016
General Data Protection Regulation (RODO)
REVIEW PAPER
The role of gut microbiota in pathogenesis of Alzheimer Disease.
1
Student’s Scientific Association of Paediatric Neurology, Medical University, Lublin, Poland
2
Department of Pediatric Neurology, Medical University, Lublin, Poland
Corresponding author
Karolina Barzyk
Student’s Scientific Association of Paediatric Neurology, Medical University, Lublin, Poland
Student’s Scientific Association of Paediatric Neurology, Medical University, Lublin, Poland
J Pre Clin Clin Res. 2025;19(3):130-136
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction and objective:
Recent insights point toward a complex interplay between gut microbiota and neurodegenerative processes in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The aim of the study is to explore how selected dietary patterns and microbiota-based interventions may affect cognitive function and neuroinflammation in AD by modulating the gut-brain axis.
Review methods:
Research was conducted based on peer-reviewed studies published mainly between 2018 – 2024, focusing on the influence of Mediterranean, high-fibre, and ketogenic diets, as well as probiotics, prebiotics, and faecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) on cognitive outcomes and inflammatory markers in AD models and patients.
Brief description of the state of knowledge:
Available evidence suggests that gut microbiota diversity and composition are altered in individuals with AD. Interventions, such as the Mediterranean or ketogenic diet, appear to enhance microbial richness and support anti-inflammatory pathways. Probiotic supplementation and FMT showed promising cognitive improvements in preclinical models, with limited but growing human data. However, considerable heterogeneity in study design and outcomes hinders firm conclusions.
Summary:
Targeting gut microbiota through diet or microbiota-modulating therapies holds promise as an adjunctive approach in AD management. While preliminary results are encouraging, there remains a pressing need for longitudinal clinical trials to clarify which microbial profiles and interventions yield the most consistent cognitive benefits. In the meantime, nutritional strategies aimed at supporting a balanced gut ecosystem may serve as a low-risk complement to conventional AD treatment.
Recent insights point toward a complex interplay between gut microbiota and neurodegenerative processes in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The aim of the study is to explore how selected dietary patterns and microbiota-based interventions may affect cognitive function and neuroinflammation in AD by modulating the gut-brain axis.
Review methods:
Research was conducted based on peer-reviewed studies published mainly between 2018 – 2024, focusing on the influence of Mediterranean, high-fibre, and ketogenic diets, as well as probiotics, prebiotics, and faecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) on cognitive outcomes and inflammatory markers in AD models and patients.
Brief description of the state of knowledge:
Available evidence suggests that gut microbiota diversity and composition are altered in individuals with AD. Interventions, such as the Mediterranean or ketogenic diet, appear to enhance microbial richness and support anti-inflammatory pathways. Probiotic supplementation and FMT showed promising cognitive improvements in preclinical models, with limited but growing human data. However, considerable heterogeneity in study design and outcomes hinders firm conclusions.
Summary:
Targeting gut microbiota through diet or microbiota-modulating therapies holds promise as an adjunctive approach in AD management. While preliminary results are encouraging, there remains a pressing need for longitudinal clinical trials to clarify which microbial profiles and interventions yield the most consistent cognitive benefits. In the meantime, nutritional strategies aimed at supporting a balanced gut ecosystem may serve as a low-risk complement to conventional AD treatment.
FUNDING
Barzyk K, Gołębiowska W, Gryta N, Brodowska A, Cieślik-Porębska M, Kondratowicz M, Kurek M, Chrościńska-Krawczyk M. The role of gut
microbiota in pathogenesis of Alzheimer Disease. J Pre-Clin Clin Res. 2025;19(3):130–136. doi:10.26444/jpccr/210031
REFERENCES (50)
1.
Varesi A, Pierella E, Romeo M, et al. The Potential Role of Gut Microbiota in Alzheimer’s Disease: from Diagnosis to Treatment. Nutrients. 2022;14(3):1–27. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu1403....
2.
Chen C, Liao J, Xia Y, et al. Gut microbiota regulate Alzheimer’s disease pathologies and cognitive disorders via PUFA-associated neuroinflammation. Gut. 2022;71(11):2233–2252. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl....
3.
Zou X, Zou G, Zou X, et al. Gut microbiota and its metabolites in Alzheimer’s disease: from pathogenesis to treatment. PeerJ.2024;12:e17061. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.....
4.
van Olst L, Roks SJM, Kamermans A, et al. Contribution of Gut Microbiota to Immunological Changes in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front Immunol. 2021;12(May):1–17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.....
5.
Liu S, Gao J, Zhu M, et al. Gut Microbiota and Dysbiosis in Alzheimer’s Disease: Implications for Pathogenesis and Treatment. Mol Neurobiol. 2020;57(12):5026–5043. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035....
6.
Montagnani M, Bottalico L, Potenza MA, et al. The Crosstalk between Gut Microbiota and Nervous System: A Bidirectional Interaction between Microorganisms and Metabolome. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(12). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24....
7.
Tang WHW, Bäckhed F, Landmesser U, et al. Intestinal Microbiota in Cardiovascular Health and Disease: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73(16):2089–2105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc....
8.
Valdes AM, Walter J, Segal E, et al. Role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. BMJ. 2018;361:36–44. https:/doi.org/10.1136/bmj.k2179.
9.
Claesson MJ, Cusack S, O’Sullivan O, et al. Composition, variability, and temporal stability of the intestinal microbiota of the elderly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(SUPPL. 1):4586–4591. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1....
10.
Chui ZSW, Chan LML, Zhang EWH, et al. Effects of microbiome-based interventions on neurodegenerative diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598....
11.
Chang L, Wei Y, Hashimoto K. Brain–gut–microbiota axis in depression: A historical overview and future directions. Brain Res Bull. 2022;182(January):44–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brai....
12.
Rutsch A, Kantsjö JB, Ronchi F. The Gut-Brain Axis: How Microbiota and Host Inflammasome Influence Brain Physiology and Pathology. Front Immunol. 2020;11(December):1–24. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.....
13.
Agirman G, Hsiao EY. SnapShot: The microbiota-gut-brain axis. Cell. 2021;184(9):2524–2524.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell....
14.
Strandwitz P. Neurotransmitter modulation by the gut microbiota. Brain Res. 2018;1693(5):128–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brai....
15.
Agustí A, García-Pardo MP, López-Almela I, et al. Interplay between the gut-brain axis, obesity and cognitive function. Front Neurosci. 2018;12(MAR):1–17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.....
16.
Wang Q, Yang Q, Liu X. The microbiota–gut–brain axis and neurodevelopmental disorders. Protein Cell. 2023;14(10):762–775. https://doi.org/10.1093/procel....
17.
Skonieczna-Żydecka K, Marlicz W, Misera A, et al. Microbiome—the missing link in the gut-brain axis: Focus on its role in gastrointestinal and mental health. J Clin Med. 2018;7(12). https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm712....
18.
Cryan JF, O’riordan KJ, Cowan CSM, et al. The microbiota-gut-brain axis. Physiol Rev. 2019;99(4):1877–2013. https://doi.org/10.1152/physre....
19.
Cowan M, Petri WA. Microglia: Immune regulators of neurodevelopment. Front Immunol. 2018;9(NOV):1–8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.....
20.
Sorboni SG, Moghaddam HS, Jafarzadeh-Esfehani R, et al. A Comprehensive Review on the Role of the Gut Microbiome in Human Neurological Disorders. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2022;35(1):1–50. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00....
21.
Fülling C, Dinan TG, Cryan JF. Gut Microbe to Brain Signaling: What Happens in Vagus Neuron. 2019;101(6):998–1002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neur....
22.
Breit S, Kupferberg A, Rogler G, et al. Vagus nerve as modulator of the brain-gut axis in psychiatric and inflammatory disorders. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9(MAR). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.....
23.
Jameson KG, Olson CA, Kazmi SA, et al. Toward Understanding Microbiome-Neuronal Signaling. Mol Cell. 2020;78(4):577–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molc....
24.
Rao M, Gershon MD. The bowel and beyond: the enteric nervous system in neurological disorders. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;13(9):517–528. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgast....
25.
Dowling LR, Strazzari MR, Keely S, et al. Enteric nervous system and intestinal epithelial regulation of the gut-brain axis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022;150(3):513–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci....
26.
Sharkey KA, Mawe GM. The enteric nervous system. Physiol Rev. 2023;103(2):1487–1564. https://doi.org/10.1152/physre....
27.
Mazzone A, Strege PR, Gibbons SJ, et al. microRNA overexpression in slow transit constipation leads to reduced Na V 1.5 current and altered smooth muscle contractility. Gut. 2020;69(5):868–876. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl....
28.
Ayyanar MP, Vijayan M. A review on gut microbiota and miRNA crosstalk: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. GeroScience. 2024;47(1):339–385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357....
29.
Khezri MR, Yousefi K, Zolbanin NM, et al. MicroRNAs in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease: an overview. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59(3):1589–1603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035....
30.
Diaz-Garrido N, Cordero C, Olivo-Martinez Y, et al. Cell-to-Cell Communication by Host-Released Extracellular Vesicles in the Gut: Implications in Health and Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22....
31.
Nakata K, Sugi Y, Narabayashi H, et al. Commensal microbiota-induced microRNA modulates intestinal epithelial permeability through the small GTPase ARF4. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(37):15426–15433. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M1....
32.
Zhao L, Ye Y, Gu L, et al. Extracellular vesicle-derived miRNA as a novel regulatory system for bi-directional communication in gut-brain-microbiota axis. J Transl Med. 2021;19(1):202. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967....
33.
Liu P, Wu L, Peng G, et al. Altered microbiomes distinguish Alzheimer’s disease from amnestic mild cognitive impairment and health in a Chinese cohort. Brain Behav Immun. 2019;80(May):633–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.....
34.
Vogt NM, Kerby RL, Dill-McFarland KA, et al. Gut microbiome alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598....
35.
Cammann D, Lu Y, Cummings MJ, et al. Genetic correlations between Alzheimer’s disease and gut microbiome genera. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598....
36.
Nguyen NM, Cho J, Lee C. Gut Microbiota and Alzheimer’s Disease: How to Study and Apply Their Relationship. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24....
37.
Kinney JW, Bemiller SM, Murtishaw AS, et al. Inflammation as a central mechanism in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement Transl Res Clin Interv. 2018;4:575–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trci....
38.
Bairamian D, Sha S, Rolhion N, et al. Microbiota in neuroinflammation and synaptic dysfunction: a focus on Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegener. 2022;17(1):1–23. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024....
39.
Thakur S, Dhapola R, Sarma P, et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s Disease: Current Progress in Molecular Signaling and Therapeutics. Inflammation. 2023;46(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753....
40.
Batista CRA, Gomes GF, Candelario-Jalil E, et al. Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammation as a Bridge to Understand Neurodegeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(9):2293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20....
41.
Asti A, Gioglio L. Can a bacterial endotoxin be a key factor in the kinetics of amyloid fibril formation? J Alzheimer’s Dis. 2014;39(1):169–179. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-13....
42.
Bossù P, Cutuli D, Palladino I, et al. A single intraperitoneal injection of endotoxin in rats induces long-lasting modifications in behavior and brain protein levels of TNF-α and IL-18. J Neuroinflammation. 2012;9(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2....
43.
Zhao Y, Cong L, Lukiw WJ. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) accumulates in neocortical neurons of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) brain and impairs transcription in human neuronal-glial primary co-cultures. Front Aging Neurosci. 2017;9(DEC):1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.....
44.
Brunt VE, LaRocca TJ, Bazzoni AE, et al. The gut microbiome–derived metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide modulates neuroinflammation and cognitive function with aging. GeroScience. 2021;43(1):377–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357....
45.
Yang J, Liang J, Hu N, et al. The Gut Microbiota Modulates Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s Disease: Elucidating Crucial Factors and Mechanistic Underpinnings. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024;30(10). https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.70....
46.
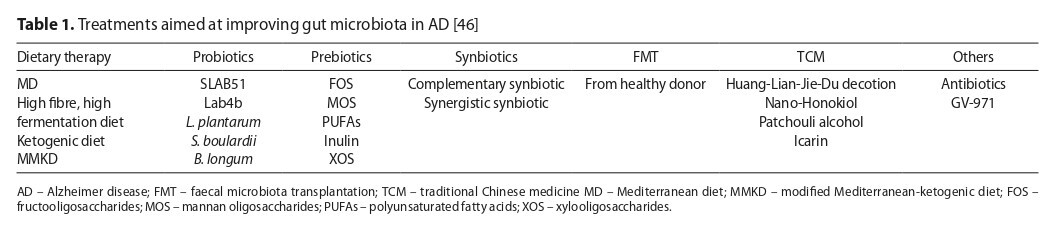
Zhou XP, Sun LB, Liu WH, et al. The complex relationship between gut microbiota and Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review. Ageing Res Rev. 2025;104(October 2024):102637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.....
47.
Thakkar A, Vora A, Kaur G, et al. Dysbiosis and Alzheimer’s disease: role of probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023;396(11):2911–2923. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210....
48.
Liu Q, Xi Y, Wang Q, et al. Mannan oligosaccharide attenuates cognitive and behavioral disorders in the 5xFAD Alzheimer’s disease mouse model via regulating the gut microbiota-brain axis. Brain Behav Immun. 2021;95(January):330–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.....
49.
Zhang S, Lu J, Jin Z, et al. Gut microbiota metabolites: potential therapeutic targets for Alzheimer’s disease? Front Pharmacol. 2024;15(September):1–30. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.....
50.
Fan X, Liu B, Zhou J, et al. High-Fat Diet Alleviates Neuroinflammation and Metabolic Disorders of APP/PS1 Mice and the Intervention With Chinese Medicine. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021;13(June):1–17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.....
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.